
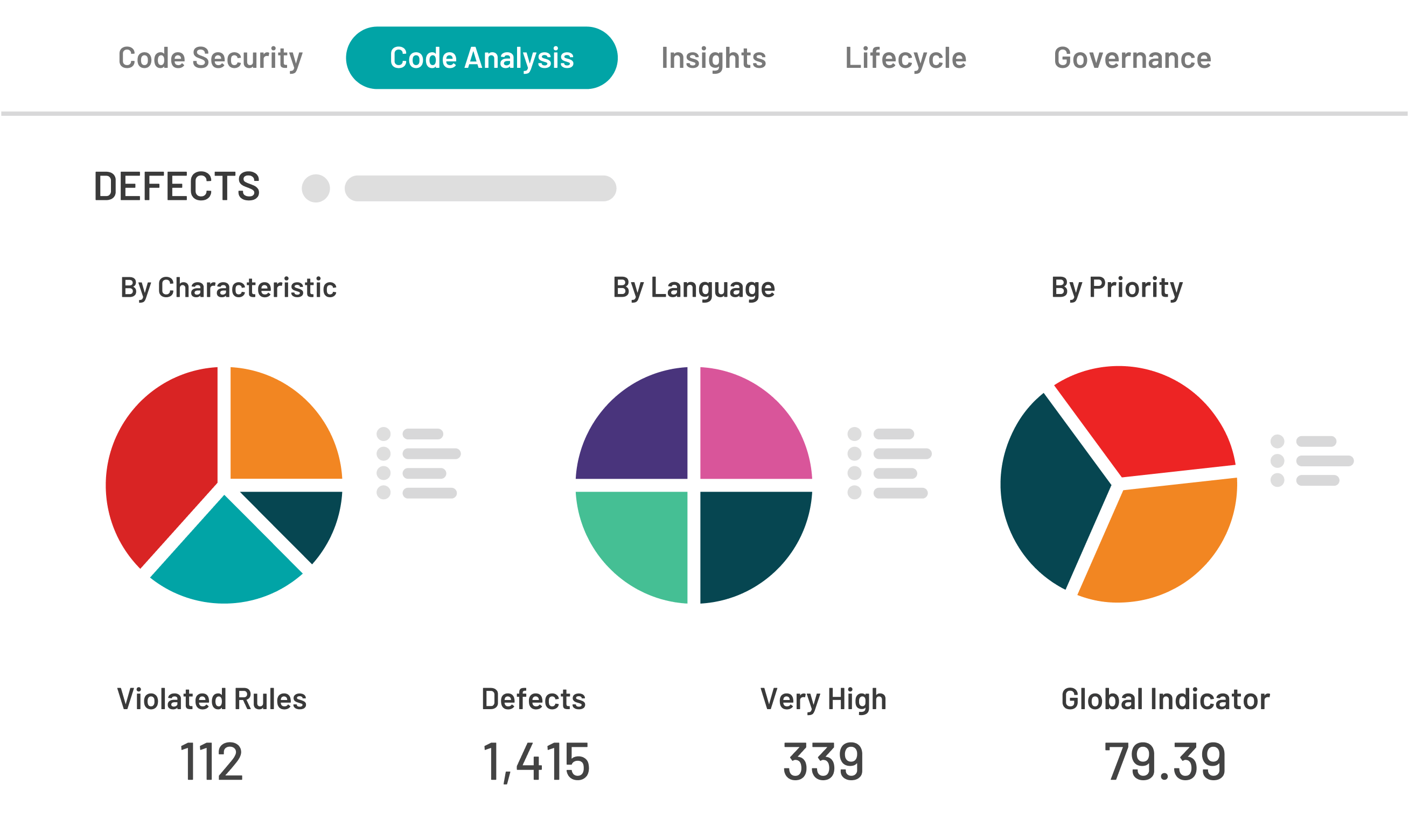
Application security is no longer an afterthought. Developers now prioritize security due to the exponential risk of cybercrime. Developers need to pay more attention to security as it is a crucial aspect of app development. Application security solutions like Kiuwan ensure that vulnerabilities are identified and resolved in a timely manner. Popular solutions like Static Application Security Testing (SAST) simultaneously used with Static Code Analysis (SCA) ensures that commonly found vulnerabilities are identified for a secure Software Development Life Cycle (SDLC). Comprehensive integration for web and mobile applications in Swift allows individual developers and leading application development organizations to mitigate sophisticated malware. SCA is the most efficient and comprehensive means of identifying loopholes, ensuring that applications are protected. Every IT organization should require SAST for developing and producing applications.
Swift is a programming language introduced at Apple’s Worldwide Developers Conference (WWDC) in 2014. Although initially proprietary, this de facto programming language is now open source, multi-paradigm, and general-purpose. It is a popular programming language among developers because it is compatible with iOS, macOS, watchOS, tvOS, and Linux. Developers can use this language to program the server-side and client-facing interface. Below are common mistakes when developing Swift applications.
Local data in an application could be stored insecurely, giving attackers a way to manipulate application directories. The locally stored data might be the user’s data or execution metadata that users cannot access. But the fact that it is not visible to application users does not mean it is invaluable. Because of the incorrect premise, a developer might make a decision that enables sophisticated malware to easily manipulate the application’s vulnerabilities.
Software is available that can view all application directories, violating privacy or stealing identities. Such attacks damage the reputations of IT organizations and have far more severe impacts on the business as a whole. Since a keychain is limited to small amounts of data, the application’s sensitive data should be encrypted to prevent attackers from manipulating plain file systems and databases. As a developer, you should only store data you need to minimize risk, since what is not stored cannot be stolen. All in all, remember not to roll your cryptography.
Aside from storage, communication can also be insecure for mobile and web applications. Reverse geocoding of back-end servers is possible when developers do not use secure communication channels. Using the HTTP protocol to transfer XML, JSON, and many other messages makes it easy for attackers to cause interference between the client and the server. It is recommended that developers use HTTPS (HTTP over SSL/TLS) to ensure that data in transit is not stolen or modified. When an attacker tampers with exchange data, there is no guarantee of who the application is communicating with.
Man-in-the-middle (MitM) attacks, which are third-party interferences between the server and the client, can be mitigated by purchasing a valid SSL certificate. There is no excuse for using insecure communication since SSL certificates are now free, unlike when they were expensive. Besides, from an implementation standpoint, there is no difference between HTTPS and HTTP. HTTPS adoption, enabled by valid SSL certificates, ensures secure communication for applications.
Application source code can be exploited to create counterfeit applications. This is a critical mobile app weakness, as attackers have the time and the technique to reverse-engineer an application through code vulnerabilities. Below are actions developers can take to ensure attackers cannot modify applications at will.
Using security tools like Kiuwan to improve Swift support ensures the application can detect violations of code integrity. This is a critical security weakness because all an attacker needs to do is download the official application from the official app store. The successful installation of a counterfeit application makes it available for download on the official download site. The unfortunate user who downloads this application is at risk of identity theft and other privacy violations. A correctly coded application should be able to detect at run time that code has been added or that its integrity has been changed.
This common mobile application mistake allows attackers to interfere with back-end servers. Since applications are human-computer interfaces, they must be backed by a back-end server. Attackers use a proxy to manipulate Insecure Direct Object References (IDOR) to inspect HTTP traffic. This basic yet common mistake leaves an application vulnerable to malware attacks. Access control can only be effective when enforced in a trusted server-side code to ensure that an attacker cannot modify the access control check.
This common security weakness makes it easy for attackers to exploit the application’s less secure environment. Extraneous functionality is something attackers are usually looking for, and it is left behind when applications are packed for production. Application configurations must be inspected to prevent this vulnerability to ensure no dead code. Common patterns associated with extraneous functionality include code, development environments, and debugging flags. This security weakness gives attackers detailed insight into how the back-end server operates. Not to forget that access to less secure application environments increases the attack surface. Aside from removing all dead code before packing the application, a developer should also identify hidden switches or flags that could give attackers access to the back-end server.
Swift is an open-source, multi-paradigm language that allows developers to create web and mobile applications. Technological advancements also mean attackers have more sophisticated techniques to tamper with applications, so developers need to avoid these common security mistakes to ensure that the applications they produce are secure. Security tools like Kiuwan Code Security enhance Swift’s security to ensure attackers cannot manipulate applications at will.


