For many modern QA teams, their role is expanding beyond just finding bugs and validating features. More and more, teams are being asked to contribute to or even take ownership of the security and compliance readiness of their software.
But the reality is that most QA teams aren’t fully prepared to take on this responsibility. Some lack dedicated security roles, while others lack the right tools.
This raises an important question: if QA teams aren’t actively contributing to application security, then who is?
Application security and compliance are no longer “nice to have,” they are fundamental to modern software development. Security can’t be retrofitted later, and testing teams must align with security risks and compliance requirements from the very beginning—not just focus on functionality.
What are some of the forces driving this shift? Influences include increasing regulatory pressure, heightened customer trust expectations, and more frequent and sophisticated supply chain attacks.
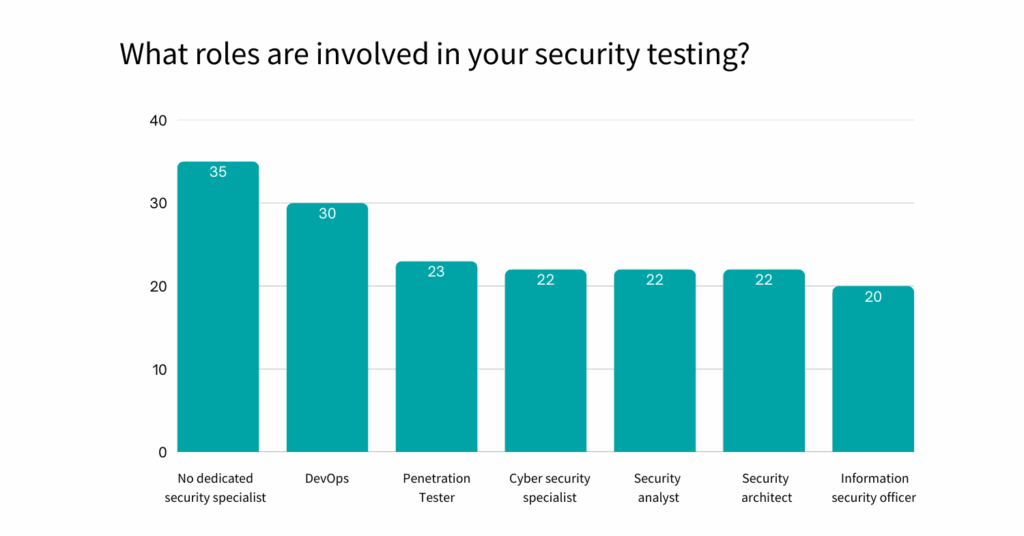
Still, 35% of QA teams lack a dedicated security role. Instead, they depend on DevOps, compliance teams, or even third-party vendors. But when security responsibility is scattered like this, it often results in no one truly owning it.
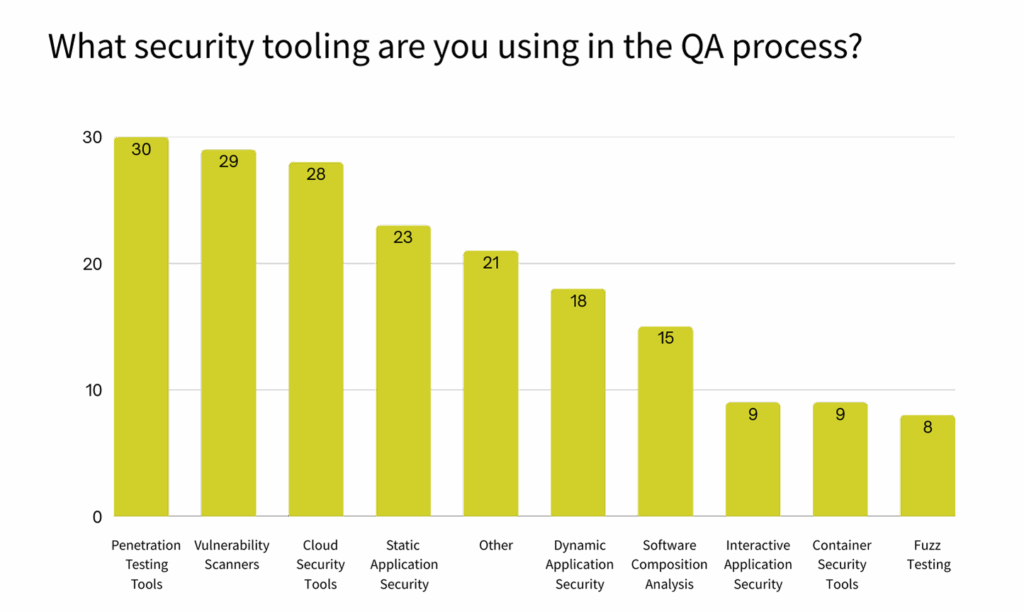
Security testing tools are no longer niche, but adoption remains patchy. According to data from the 4th Edition Software Testing and Quality Report (4E STQR), 30% of respondents don’t use any security testing tooling at all! Meanwhile, 30% use penetration testing, 29% rely on vulnerability scanners, and 23% use Static Application Security Testing (SAST).
Early adoption of SAST and dependency scanning, which is the classic shift-left approach, offers massive value—especially as cloud adoption and AI-driven systems expand attack surfaces. However, even with shift-left, clear ownership of security tasks still needs to be defined.
According to the 4E SQTR, 31% of respondents say compliance standards don’t apply to them. But even in unregulated industries, regional laws like GDPR and CCPA, customer requirements and expectations, and supply chain security mandates make proactive compliance essential
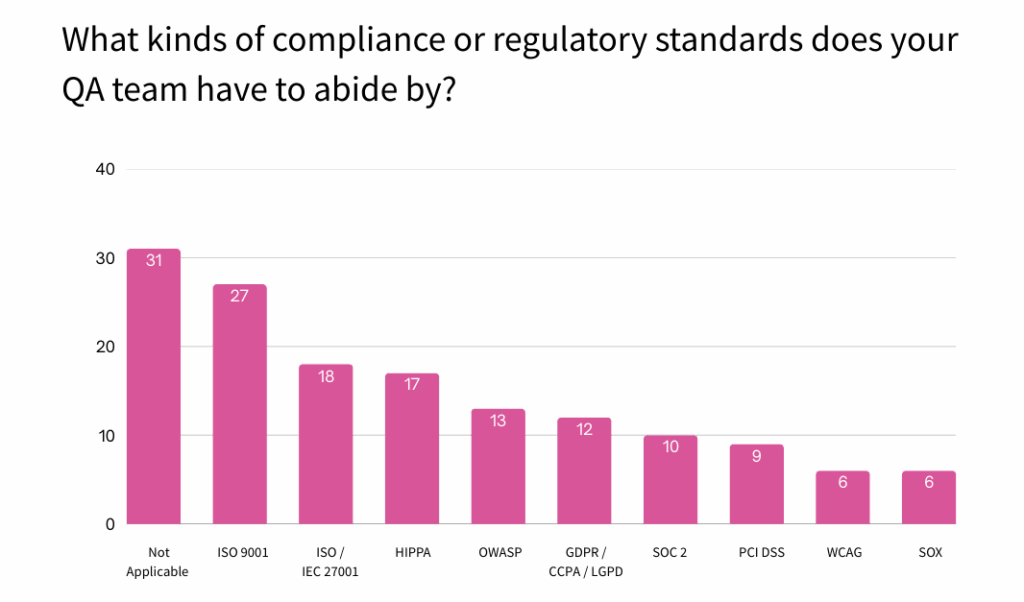
Respondents identify common standards such as ISO 9001, ISO 27001, and HIPAA not just as compliance mandates, but as trust and resilience baselines.
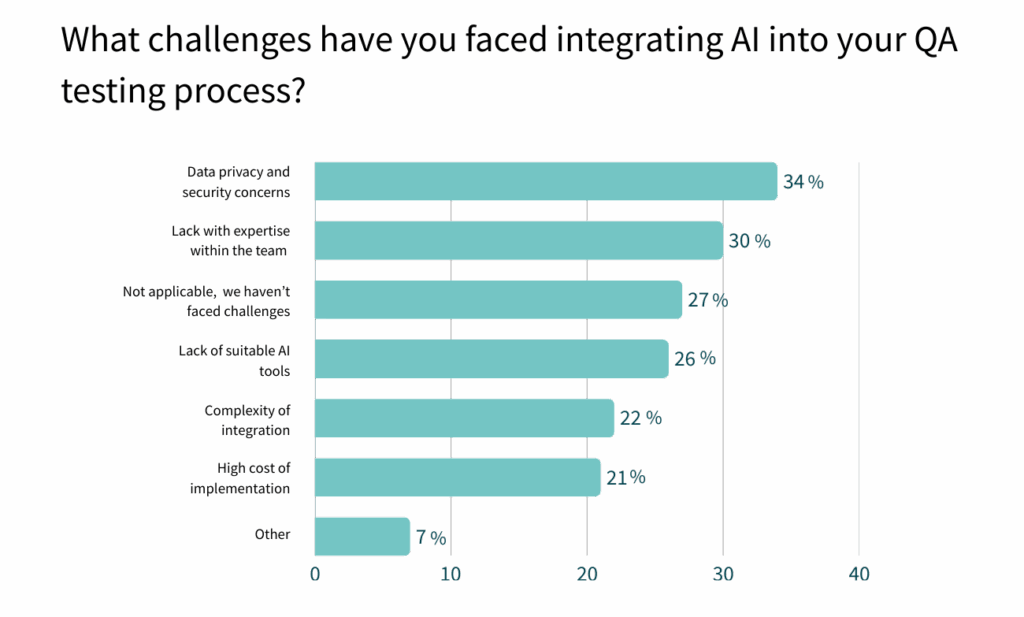
AI is already impacting QA, but security remains a major hurdle. 34% of respondents see data privacy and security concerns as barriers to adopting AI in their QA testing processes.
The biggest opportunities? AI-powered predictive defect analysis and risk-based testing, which leverage historical vulnerabilities, past test data, and code change history to predict where problems are likely to emerge. Looking ahead, predictive AI could even flag high-risk third-party components—especially those with outdated or conflicting libraries—before they become points of failure.
But relying solely on AI-predictive testing is risky. A more resilient approach pairs predictive insights with established security tooling like SAST, so AI-identified hotspots receive immediate code-level verification. This combination can help close critical gaps before code reaches production.
Where QA leaders should focus now:
Code security readiness in QA isn’t just about adding another checklist; it’s a mindset shift. Teams that embed security and compliance into how they test, ship, and maintain software won’t just pass audits—they’ll become a critical line of defence in their organizations’ overall security posture.
For deeper insights and detailed data on security readiness in QA and other key software quality trends, read the full 4th Edition Software Testing and Quality Report. Ready to strengthen your security testing? Try Kiuwan free and see how it can help your team build proactive compliance and secure software from the start.