You are viewing an old version of this page. View the current version.
Compare with Current View Page History
« Previous Version 98 Next »
Introduction
The Kiuwan On-Premises installer is a powerful tool that suits multiple environment scenarios:
- Single-host fully contained installation.
- Multi-host installation where infrastructure services are externalized.
- Multi-host installation where Kiuwan services are distributed.
- Any combination of the two previous scenarios.
Depending on your needs, a different installation approach will be needed. Check this installation guide for details on how to proceed and to find the solution that best fits your requirements.
System requirements
Installation requirements
It is mandatory for any host where Kiuwan On-Premises is installed to meet these requirements:
- Linux distribution
- Linux kernel version 3.10 or higher
- Connectivity to SMTP Mail Server.
- Internet connectivity during the installation process (see Needed internet connections).
- Installing user must be root or have sudo privileges.
Please follow Docker official recommendations when installing Docker. These URLs describe the installation process for different Linux distributions:
These softwares are also needed:
- Docker CE >= 19.03.2
- Docker-compose >= 1.24.1
- Unzip
- GNU tar
- Wget
- BC
- Tee
- Java Runtime Environment >= 8 (needed to generate keystores for custom hosts).
- OpenSSL >= 1.1.1 (needed to generate certificates for custom hosts). Other supported versions of OpenSSL are 1.0.2g and 1.0.2k-fips.
Make sure that the docker-compose command can be executed with sudo. This means that the docker-compose binary file must be included in the sudoers path. The binary is usually installed under the /usr/local/bin directory. Depending on your OS, this information may be set in the secure_path variable in the sudoers file (/etc/sudoers). Please check the official Docker-compose documentation for more information: https://docs.docker.com/compose/install.
It is also recommended to use the target installation hosts exclusively for Kiuwan services. If you plan on running other containers than Kiuwan's in a single-host installation, please make sure that:
- None of them is using the following network: 172.172.0.0/16
- There are not containers that may block any of these ports:
- 443: standard HTTPS port (or the one you will configure to access your Kiuwan On-Premises installation).
- 8143, 8243, 8343, 8443, 8543, 8643, 8743, 8843: ports that Kiuwan front instances listen to.
- 6379: port that Redis instances listen to.
- 3306: port that MySQL instance listen to.
Special requirements for RedHat, CentOS and Fedora
If your docker server is running on RedHat, CentOS or Fedora, be sure the filesystem where docker is installed supports d_type (the directory entry data structure that describes the information of a directory on the filesystem).
Some of the above operating systems are not configured with d_type support (see http://www.pimwiddershoven.nl/entry/docker-on-centos-7-machine-with-xfs-filesystem-can-cause-trouble-when-d-type-is-not-supported.
Running on XFS without d_type support causes Docker to skip the attempt to use the overlay or overlay2 driver. See https://docs.docker.com/storage/storagedriver/overlayfs-driver/#prerequisites.
You can check if your existing XFS filesystem has d_type enabled by running the following commands:
$ docker info | grep "Supports d_type:" Supports d_type: true $ xfs_info /docker-mount-point | grep ftype naming =version 2 bsize=4096 ascii-ci=0 ftype=1
In case you get d_type: false or ftype=0, you will need to create a new XFS filesystem with d_type support enabled. Unfortunately, it isn't possible to enable d_type support on an existing filesystem.
There are two options:
- Add a new disk and create a new XFS partition on it.
- Backup your existing data and recreate the XFS filesystem with d_type support enabled.
You can create a new XFS filesystem with d_type enabled by running the following command:
$ mkfs.xfs -n ftype=1 /mount-point
Needed internet connections
Please make sure your host machines have connection to these servers when installing Kiuwan On-Premises:
| Host | Needed when | Purpose |
|---|---|---|
*.docker.com (all subdomains of docker.com, including nested subdomains) *.docker.io (all subdomains of docker.io) | Installing | These are the Docker servers where the needed images will be pulled from. |
| cdn.mysql.com | Installing | Download the mysql driver file needed during the installation process. |
| static.kiuwan.com | Installing | This is Kiuwan's static content server, needed by the installer to download needed resources. |
| api.kiuwan.com | You own a Kiuwan On-Premises Insights license, both for installing and running | This is Kiuwan's central API endpoint, needed to update Insights vulnerabilities database. |
Proxy configuration
If the host on which you are installing Kiuwan On-Premises needs to access the internet through a proxy server, note that:
- Your OS should know about your proxy settings in order to be able to download the Kiuwan On-Premises installer distribution.
- Docker daemon must know about your proxy settings in order to download images from https://*.docker.com or https://*.docker.io
- Docker must know about your proxy settings in order to propagate them to the created containers.
- Direct access to your SMPT mail server is needed (it is MANDATORY that the host machine can access your mail server regardless of the proxy server).
To instruct your OS to use your proxy settings, please refer to the official documentation for your Linux distribution.
To make Docker daemon use your proxy server, please follow the official Docker documentation on how to set a proxy:
https://docs.docker.com/config/daemon/systemd/#httphttps-proxy
To make Docker use your proxy when creating containers, please follow the official Docker documentation on how to set a proxy to be used by the containers:
https://docs.docker.com/network/proxy/#configure-the-docker-client
Remember to restart both docker daemon and docker to apply proxy configuration changes:
sudo systemctl daemon-reload sudo systemctl restart docker
You can check if Docker has successfully read your configuration by executing:
docker system info
Check if your proxy configuration is shown in the console:
[...] HTTP Proxy: http://proxy.domain.com:3456 HTTPS Proxy: http://proxy.domain.com:3456 No Proxy: localhost,127.0.0.1,172.172.0.0/16 [...]
Examples
This is an example of a /etc/systemd/system/docker.service.d/http-proxy.conf file that makes the Docker daemon use a proxy:
[Service] Environment="HTTP_PROXY=http://user:password@proxy.domain.com:3456" Environment="HTTPS_PROXY=http://user:password@proxy.domain.com:3456" Environment="NO_PROXY=localhost,127.0.0.1,172.172.0.0/16"
This is an example of a ~/.docker/config.json that makes Docker propagate proxy configuration to the created containers:
{
"proxies": {
"default": {
"httpProxy": "http://user:password@proxy.domain.com:3456",
"httpsProxy": "http://user:password@proxy.domain.com:3456",
"noProxy": "localhost,127.0.0.1,172.172.0.0/16"
}
}
}
CPU and memory minimum requirements
The following table shows the minimum requirements for each service. Note that these are only minimum requirements. You should make sure to give each service enough resources depending on your system demands.
| Service | Memory | CPU cores |
|---|---|---|
| wildflykiuwan-f[n] | 2.5GB | 2 cores |
| wildflykiuwan-a[n] | 2.5GB per analysis slot | 2 cores per analysis slot |
| wildflykiuwan-s[n] | 2.5GB | 2 cores |
| mysql | 5GB | 4 cores |
| loadbalancer | 1GB | 1 core |
| redis_0000[n] | 2GB | 2 cores |
Note: CPU clock speed and disk speed will affect the overall response time.
With the above configuration, a system with the following load should give continuous service without problems:
- Parallel processing of 2 analyses (any additional parallel analysis request will be enqueued, and it will be executed as soon as any of the running analyses finishes)
- 50 concurrent web users or REST API calls.
Given the table above, for a single-host installation where no service is externalized the minimum system requirements are:
- 18GB of RAM and a processor with 8 cores for Kiuwan On-Premises.
It is recommended that you overscale these characteristics for the OS to have resources available for itself.
The Kiuwan On-Premises installation tool (kiuwan-cluster)
The Kiuwan On-Premises installation process is carried out by our "kiuwan-cluster" tool.
The tool is provided as a tar.gz file. The following table summarizes the resources you will find once the tool distribution is extracted:
| Resource | Purpose |
|---|---|
| /config/volumes.properties | Configuration file to set where your persistent volumes will reside. |
| /docker/compose | Docker compose files used to manage Kiuwan On-Premises' docker services. |
| /docker/*.sh | Advanced shell scripts to interact with your Kiuwan On-Premises installation. |
| /logs | The folder where the tool will write installation logs. |
| /ssl | Tools that ease the certificate creation to keep Kiuwan On-Premises under a secure environment. |
| /support | Tools to ease collecting support data. |
| /tools | Internal tools used when installing. |
| /user-content | The folder where you will have to put some resources the installation process will need. |
| /volumes | The base persistent volumes (that may be copied to different locations depending on your installation needs). |
*.sh | Main shell scripts to interact with your Kiuwan On-Premise installation. |
The following sections will guide you through the installation process.
Installation: common steps
This guide will reference two important folders:
- [INSTALLER_DIR]: where the installation tool (kiuwan-cluster) will be located.
- [VOLUMES_DIR]: where the persistent volumes will be located.
Sometimes these folders will be referenced inside command line examples. Please make sure you replace any of them with the needed real path.
Note that it is up to you where these folders will be located.
Step 1: download kiuwan-cluster
The first step is to download kiuwan-cluster (the Kiuwan On-Premises installation tool). It can be downloaded directly from a terminal like this:
wget https://static.kiuwan.com/download/onpremise/kiuwan-cluster.tar.gz
This will download the latest available installation tool to the current directory.
Note that, as stated in System requirements, you will need access to static.kiuwan.com in order to download this file. Check your proxy configuration if you access the internet over a proxy server as well.
Step 2: untar kiuwan-cluster
Once downloaded, you should untar the provided gz file:
tar xvzpf kiuwan-cluster.tar.gz
This will untar the installation tool to a folder with extended version information of the tool. For example:
/home/user/kiuwan-cluster_master.XXXX-2.8.YYMM.V
This folder will be referred to as [INSTALLER_DIR] throughout this guide.
Step 3: copy license files
In order to be able to start a Kiuwan On-Premises installation, you will need two license files:
- configq1.zip
- license.zip
Copy these files to the user-content folder of your installation tool directory (please remember to replace [INSTALLER_DIR] with the real location of your installation directory):
cp configq1.zip [INSTALLER_DIR]/user-content cp license.zip [INSTALLER_DIR]/user-content
Step 4: download and copy the needed driver version for MySQL
Kiuwan On-Premises needs this exact MySQL driver:
mysql-connector-java-5.1.39-bin.jar
You can download it by executing this command and extracting the jar file included inside the tar:
wget https://cdn.mysql.com/archives/mysql-connector-java-5.1/mysql-connector-java-5.1.39.tar.gz
Untar the downloaded file:
tar xvzpf mysql-connector-java-5.1.39.tar.gz
Copy the connector jar file to the user content folder:
cp mysql-connector-java-5.1.39/mysql-connector-java-5.1.39-bin.jar [INSTALLER_DIR]/user-content
Step 5: configure the volumes paths
The installation tool provides the base volumes needed to boot a first installation of Kiuwan On-Premises. Three volumes are included:
- config-shared: contains the base configuration, shared between different services.
- data-shared: contains the base data structure, shared between different services.
- data-local: contains the base data structure, independent for each service.
The installation tool needs to know where you want these volumes to reside. To do so, edit the file located in [INSTALLER_DIR]/config/volumes.properties and set desired locations:
config.shared=[VOLUMES_DIR]/config-shared data.shared=[VOLUMES_DIR]/data-shared data.local=[VOLUMES_DIR]/data-local
Please remember that [VOLUMES_DIR] is just a placeholder for the real path you chose.
Note that you will need to create the configured folders by running:
sudo mkdir [VOLUMES_DIR]
In case you are using different base directories for each volume, you must create all the needed base directories.
Step 6: initialize your volumes
Copy the provided volumes to the configured location by running this script:
cd [INSTALLER_DIR] sudo ./deploy-volumes.sh
Step 7: configure your email server
Kiuwan On-Premises needs a working and accessible e-mail server to send notifications.
Edit with your preferred editor the main configuration file, found in your [VOLUMES_DIR]:
sudo vim [VOLUMES_DIR]/config-shared/globalConfig/globalConfig.properties
Please note that this is the file located in your [VOLUMES_DIR], not in the [INSTALLER_DIR], which only contains the base volumes.
Edit the following properties under the section named "Kiuwan instances shared configuration":
kiuwan.mail.host: the host of your email server.
kiuwan.mail.port: the port of your email server.
kiuwan.mail.username: the username to use when authenticating with your email server (set to empty if no username is needed for your email server).
kiuwan.mail.password: the password to use when authenticating with your email server (set to empty if no password is needed for your email server).
kiuwan.mail.from: the email account to use as the sender.
- kiuwan.mail.secure.layer: the security layer that your mail server uses (ssl or tls).
- kiuwan.default.mail.account: the email account to set to your default Kiuwan user.
Installation: single-host and minimum configuration
Follow this section if you want to proceed and install Kiuwan On-Premises with no further customization.
The defaults will install Kiuwan On-Premises with these characteristics:
- Single-host installation, including these services (see Kiuwan On-Premises Distributed System Architecture for more details):
- Apache as a load balancer.
- A Kiuwan front instance.
- A Kiuwan analyzer instance.
- A Kiuwan scheduler instance.
- MySQL database.
- Redis cluster.
- HTTPS support when accessing Kiuwan and between the loadbalancer and Kiuwan instances.
- Kiuwan On-Premises deployed in the default domain (https://kiuwan.onpremise.local).
If this is enough for you, just continue with the following steps.
If you plan to change the default domain, please refer to the Modifying the default domain section before continuing and come back here after you have made the needed changes.
Step 1: deploy user content
On a terminal, navigate to the [INSTALLER_DIR] folder and execute this command:
sudo ./deploy-user-content.sh
This will copy the user-content files to the configured volumes and set the needed permissions.
Step 2: install Kiuwan On-Premises
On a terminal, navigate to the [INSTALLER_DIR] folder and execute this command:
sudo ./install.sh
This will:
- Check if your host meets the minumum installation requirements.
- Download and run the needed Docker images.
- Install the database resources for Kiuwan On-Premises.
- Download the latest available Local Analyzer, Engine and Kiuwan for Developers to make them available in your installation.
- Install the engine data in your Kiuwan On-Premises database.
- Autogenerate the needed configuration for each Kiuwan instance.
- Run all the needed containers.
Once the installation is finisished please refer to the Accessing your Kiuwan On-Premises installation section.
Installation: modifying the default domain
The default configuration sets "kiuwan.onpremise.local" as the default domain to access Kiuwan On-Premises.
We encourage to change the default domain, but take into account that this means updating the provided certificates to keep your installation connections secure.
Step 1: edit the global configuration file
Using your preferred editor, open the default configuration file located in your config-shared volume:
sudo vim [VOLUMES_DIR]/config-shared/globalConfig/globalConfig.properties
Edit these properties (kiuwan.port is only needed if you want to use https under a different port than the default 443):
- kiuwan.domain
- kiuwan.port
Step 2: update load balancer configuration
Once you have selected your new domain and if you are using the provided Apache load balancer, you should edit the main Apache configuration file:
sudo vim [VOLUMES_DIR]/config-shared/ApacheLoadBalancer/conf/httpd.conf
Edit this line and change the default domain (kiuwan.onpremise.local) to your new domain:
Define kiuwanDomain kiuwan.onpremise.local
If you have externalized the provided Apache load balancer, you should edit the equivalent configuration file to set the new domain.
Step 3: generate new certificates
Please refer to the Managing certificates guide and follow the needed steps depending on your needs.
Once this is done, you should have these files under the [INSTALLER_DIR]/user-content/certs folder:
- cacert.pem
- domainkey.pem
- domaincert.pem
- domainkeystore.jks
- truststore.jks
Step 4: complete your installation
If you are performing a new Kiuwan On-Premises installation, please refer to the steps indicated in the following sections, depending on your installation needs:
If you have already installed Kiuwan On-Premises, you will need to stop your containers, update the deployed configuration and restart them. To do so, execute these commands:
cd [INSTALLER_DIR] sudo ./stop-all.sh cd [INSTALLER_DIR]/docker sudo ./update.sh cd [INSTALLER_DIR] sudo ./start-all.sh
Step 5: update your DNS or hosts files
If you are modifying an existing Kiuwan On-Premises installation, you will need to update your DNS or hosts files.
Note that if you have generated new certificates signed by a different CA than the one that signed the previous ones, you should update your Kiuwan On-Premises clients certificates or truststores.
Please refer to Accessing your Kiuwan On-Premises installation for details on these topics.
Installation: externalizing services
Kiuwan On-Premises uses three main services under its infrastructure's hood:
- Apache: used as a load balancer when multiple Kiuwan frontal instances are running.
- Redis: an in-memory cache to speed up response times.
- MySQL: Kiuwan's main database.
If you want to use your own services for any of the previous ones, Kiuwan On-Premises can connect to them by bypassing their creation at installation time.
Configuring services to externalize
First of all, you will need to edit the main configuration file and mark which services you want to externalize:
- [VOLUMES_DIR]/config-shared/globalConfig/globalConfig.properties
This table shows the properties you should modify when externalizing each service:
| Service | Property | Default value |
|---|---|---|
| Apache | kiuwan.externalize.apacheloadbalancer | false |
| Redis | kiuwan.externalize.redis.[cache|storage] | false |
| MySQL | kiuwan.externalize.mysql | false |
When setting to "true" any of the previous properties, the corresponding service will be externalized and the installation tool will not manage any related instance. Note that all the configuration will be up to you, as the Kiuwan On-Premise installer will only be able to configure how Kiuwan On-Premise will connect to your own services.
Externalizing Apache
When externalizing this service you should take into account that:
- Each Kiuwan On-Premises frontal instance domain name is wildflykiuwan-f[n], [n] being the frontal instance number. Note that depending on your installation needs you may want to access each instance via IP or its own host name.
- Each Kiuwan On-Premises frontal instance only exposes the port 8[n]43 for https traffic, [n] being the frontal instance number.
- You should provide your frontal service the needed certificates in order to make https connections available (please refer to Managing certificates for more information):
- domaincert.pem
- domainkey.pem
- cacert.pem
Externalizing Redis
In case you set Redis as an external service, Kiuwan On-Premises needs to know where the Redis nodes are deployed and which ports to use when connecting to them.
In case you use a special DNS that can resolve the same host to different hosts and ports (DNS Round-Robin or equivalent), you should configure just an single host.
All the needed configuration is located in the main configuration file:
- [VOLUMES_DIR]/config-shared/globalConfig/globalConfig.properties
The following table shows the properties to configure (note that you should set exactly the same configuration for both "cache" and "store" Redis configurations):
| Property | Meaning | Example |
|---|---|---|
| redis.[cache|store].nodes | Comma separated list of host and port for each Redis node | rn1.mydomain.com:6379,rn2.mydomain.com:6379,rn3.mydomain.com:6379,rn4.mydomain.com:6379,rn5.mydomain.com:6379,rn6.mydomain.com:6379 |
| redis.[cache|store].timeout | Connection timeout in milliseconds | 2000 |
| redis.[cache|store].password | Password to use when connecting to a node (leave empty if you have set no password access) | |
| redis.[cache|store].clientName | Name of the client connection (defaults to empty) |
It is mandatory for Kiuwan On-Premises to work with your Redis installation that it complies with these characteristics:
- Redis version must be equal or higher than 5.0.4.
- Redis must be configured as a cluster.
- Eviction policy must be set to "noeviction" (refer to Redis official documentation, maxmemory-policy configuration property).
Externalizing MySQL
When externalizing MySQL note that your MySQL installation should comply with these characteristics:
- MySQL version 5.7
- Maximum number of connections: 130 per Kiuwan On-Premises instance.
Step 1: create Kiuwan On-Premises schemas
You should create the needed schemas in your MySQL installation. To do so, please execute this script with a user that has schema creation privileges:
create database opt_activity CHARACTER SET utf8 COLLATE utf8_unicode_ci; create database opt_cinc CHARACTER SET utf8 COLLATE utf8_unicode_ci; create database opt_metamodel CHARACTER SET utf8 COLLATE utf8_unicode_ci; create database opt_qmm CHARACTER SET utf8 COLLATE utf8_unicode_ci; create database opt_transaction CHARACTER SET utf8 COLLATE utf8_unicode_ci; create database opt_insight CHARACTER SET utf8 COLLATE utf8_unicode_ci;
Step 2: create Kiuwan On-Premises user
You should create the user that will be connecting to Kiuwan On-Premises schemas. Please run this script as an admin user to do so:
create user '[USER]'@'%' identified by '[PASSWORD]'; grant all privileges on `opt_%`.* to '[USER]'@'%' identified by '[PASSWORD]'; flush privileges;
Note that you should replace [USER] with the desired user name and [PASSWORD] with the desired password.
Step 3: configure your installation
The following table shows the properties to configure for Kiuwan On-Premises to connect to your own MySQL instance:
| Property | Meaning | Example |
|---|---|---|
| mysql.host | Your MySQL installation host | mysqlkiuwan |
| mysql.port | The connection port to access your MySQL installation | 3306 |
| mysql.username | The user that will be connecting to Kiuwan On-Premises schemas (should match the one provided in the previous step) | csaas |
| mysql.password | The user's password (should match the one provided in the previous step) |
Installation: using Amazon S3 as file repository
Kiuwan On-Premises uses these shared file repositories to store analysis related data:
- kiuwanCentralRepository: stores analysis results files.
- kiuwanSourceCodeRepository: stores source code.
These two Kiuwan On-Premises internal file repositories can be replaced with Amazon S3 buckets.
To do so, you should first configure these properties in the main configuration file ([VOLUMES_DIR]/config-shared/globalConfig/globalConfig.properties):
- centralFileRepository.type=s3
- sourceCodeFileRepository.type=s3
The following table shows the properties you should modify when making Kiuwan On-Premises connect to AWS S3 buckets:
| Property | Meaning | Example |
|---|---|---|
s3.privateBucket.bucketName | Your AWS S3 bucket name | s3mycompany-us |
| s3.privateBucket.subDirectoryName | Your AWS S3 subdirectory name under the configured bucket | mydirectory |
| s3.privateBucket.accessKeyId | AWS access key for your bucket | BS3BX35Z27UAQCEACTPQ |
| s3.privateBucket.secretKeyId | AWS secret key for your bucket | Aasdfjklwe1234123lkjfasc21ssACasfEq124Da |
| s3.dir.centralFileRepository | The main key prefix that will be used to keep the central file repository entries | kiuwanCentralWorkingDirectory/analysisData |
| s3.dir.sourceCodeFileRepository | The main key prefix that will be used to keep the source code file repository entries | kiuwanCentralWorkingDirectory/analyzedSourceCode |
Installation: advanced configuration
All configuration properties you can edit are located in this file located inside your data-shared volume:
- [VOLUMES_DIR]/config-shared/globalConfig/globalConfig.properties
Here is a complete list of the properties you can configure and their meaning (default passwords are omitted):
| Property | Default value | Meaning |
|---|---|---|
| Access configuration | ||
| kiuwan.protocol | https | Kiuwan default access protocol |
| kiuwan.domain | kiuwan.onpremise.local | Kiuwan default domain |
| kiuwan.port | 443 | Kiuwan default access port |
| Mailing configuration | ||
| kiuwan.mail.host | Email server host | |
| kiuwan.mail.port | Email server port | |
| kiuwan.mail.username | Email server username | |
| kiuwan.mail.password | Email server password | |
| kiuwan.mail.from | Email account you want Kiuwan to use when sending emails | |
| kiuwan.default.mail.account | Email account to set to the built-in Kiuwan users | |
| Kiuwan instances shared configuration | ||
| timezone | Europe/Madrid | Kiuwan servers timezone. Please refer to Supported timezones page for a complete list of supported time zones. |
| Kiuwan front instances configuration | ||
| kiuwan.nodes.front.max.memory | 1024m | Max memory to set to front instances |
| session.timeout | 3600 | Time a session can be inactive before close it (in seconds) |
| session.secure | false | Use the secure attribute of the session cookie |
| session.httponly | false | Use the httponly attribute of the session cookie |
| Kiuwan analyzer instances configuration | ||
| kiuwan.nodes.analyzers.max.memory | 1024m | Max memory to set to analyzer instances |
| queues.reportsGeneratedQueueSize | 2 | Number of slots enabled for analysis processing |
| Kiuwan scheduler instances configuration | ||
| kiuwan.nodes.schedulers.max.memory | 1024m | Max memory to set to front instances |
| Kiuwan file repositories configuration | ||
| centralFileRepository.type | filesystem | Central file repository storage type [filesystem|s3] |
| sourceCodeFileRepository.type | filesystem | Source code repository storage type [filesystem|s3] |
| Amazon S3 bucket configuration (only applies when using AWS S3 type repositories) | ||
| s3.privateBucket.bucketName | S3 bucket name | |
| s3.privateBucket.subDirectoryName | S3 subdirectory name | |
| s3.privateBucket.accessKeyId | Access key id | |
| s3.privateBucket.secretKeyId | Secret key id | |
| s3.dir.centralFileRepository | Central file repository directory | |
| s3.dir.sourceCodeFileRepository | Source code file repository directory | |
| MySQL configuration | ||
| mysql.host | mysqlkiuwan | MySQL server host |
| mysql.port | 3306 | MySQL server port |
| mysql.username | csaas | MySQL server username |
| mysql.password | MySQL server password | |
| mysql.config.useSSL | false | Enable or disable the use of encryption when connecting to MySQL |
| mysql.config.requireSSL | false | Force the use of encryption when connecting to MySQL |
| mysql.config.verifyServerCertificate | false | Force the validation of the certificate served MySQL |
| Redis Cluster cache and store configuration | ||
| redis.[cache|store].nodes | redis_0000[1-6]:6379 | Redis nodes hosts (use the provided single host name when using elasticache) |
| redis.[cache|store].timeout | 2000 | Redis connection timeout |
| redis.[cache|store].password | Redis password | |
| redis.[cache|store].clientName | Redis client name | |
| SSL configuration | ||
| java.keystore.password | Java keystore password. This must be aligned with the generated keystore password (in case you change the default Kiuwan host name) | |
| java.truststore.password | Java truststore password. This must be aligned with the generated truststore password (in case you change the default Kiuwan host name) | |
Accessing your Kiuwan On-Premises installation
In order to access your Kiuwan On-Premises installation you should follow a few more steps.
Step 1: add your domain to your local network DNS
To access your Kiuwan On-Premises installation you should take into account whether the selected domain is available in the DNSs your local network may use.
In order to access Kiuwan you will need to do one of the following options:
- Add kiuwan.onpremise.local to your DNS (recommended option).
- Add kiuwan.onpremise.local to your hosts file.
For testing purposes or if you choose the second option, edit this file in the host where you plan to access Kiuwan from:
- Windows OS: C:\Windows\System32\drivers\etc\hosts
- Linux OS: /etc/hosts
Add the following entry to the previous file:
[kiuwan_on_premise_host_ip] [kiuwan_on_premise_host]
For example, the previous entry may look like this for an installation pointing to the default host (note that the IP of the example may change in your local network):
192.168.0.56 kiuwan.onpremise.local
Step 2: add your certificates' CA to your clients
Depending on whether you are using a trusted CA or not to sign your certificates, you may need to add the CA to your client's certificate store to avoid warning messages.
Please refer to the Adding the provided or a custom CA to Kiuwan On-Premises' clients section for a complete explanation on how to handle this depending on your installation configuration.
Step 3: access Kiuwan On-Premises
Accessing the web application
Once the previous steps have been done, you should be able to access Kiuwan On-Premises entering your Kiuwan host in your browser which by default is:
https://kiuwan.onpremise.local
Note that although the installation process may have finished, the Kiuwan servers may need some minutes to start up. If this is the case, a loading page will be shown (as long as you are using the provided Apache load balancer service):
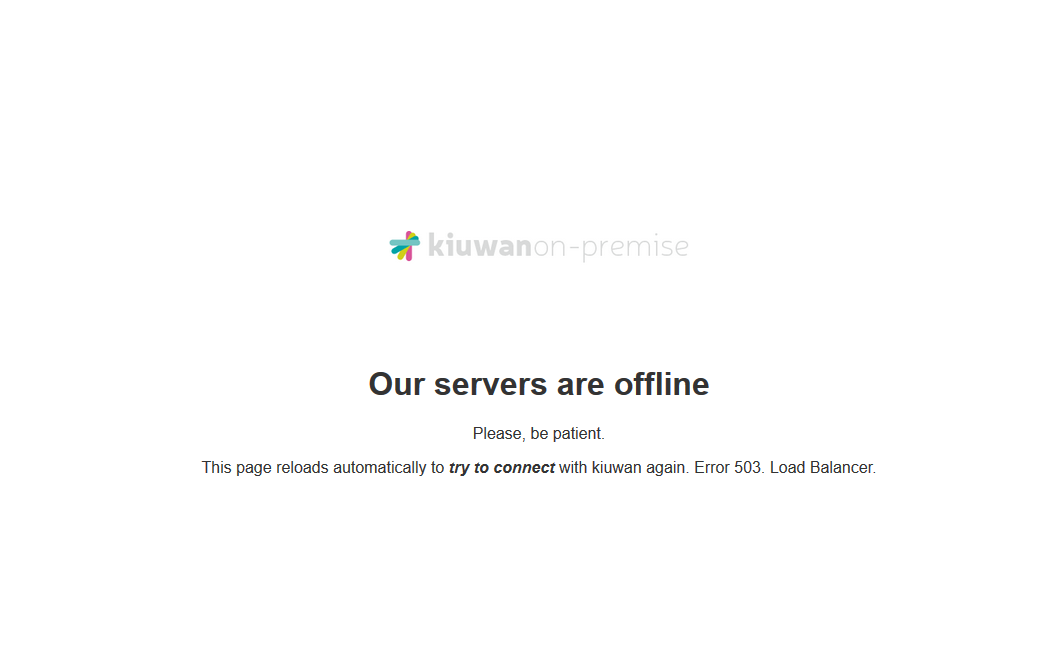
Once Kiuwan On-Premises services are started, you will be redirected to your Kiuwan On-Premises installation's main login page:
Downloading Kiuwan Local Analyzer
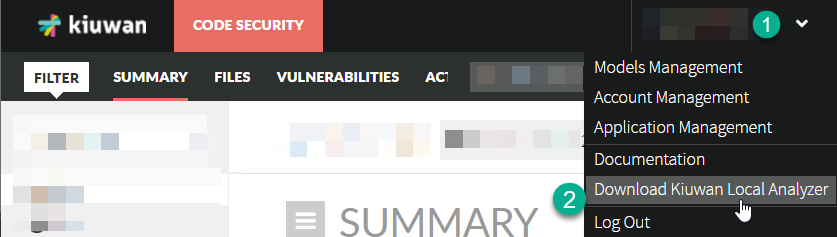
Once logged into the web application, you can download Kiuwan Local Analyzer by clicking on the "Download Kiuwan Local Analyzer" option in the top right drop-down menu.
Consuming Kiuwan REST API
To access your Kiuwan On-Premises installation via its REST API, you should point to this URL:
https://[KIUWAN_DOMAIN]/saas/rest/v1
Configuring Kiuwan for Developers
To install the Kiuwan for Developers plugin you should point to the corresponding download endpoint for each Kiuwan for Developers distribution:
| IDE distribution | How to install | URL |
|---|---|---|
| Eclipse | Add a new updatesite | https://[KIUWAN_DOMAIN]/pub/updatesite |
| JetBrains | Add a new custom plugin repository | https://[KIUWAN_DOMAIN]/pub/jetbrains/plugins.xml |
| Visual Studio | Add an extension gallery | https://[KIUWAN_DOMAIN]/pub/vsgallery/atom.xml |
| Visual Studio Code | Download the extension package file and use the "Install from VSIX" option | https://[KIUWAN_DOMAIN]/pub/vscode/k4d-vscode.vsix |
Please refer to the Kiuwan for Developers page for more information.
Default users
Kiuwan On-Premises is provided with two user accounts:
| Username | Default password |
|---|---|
| sysadmin | sysadmin |
| kiuwanadmin | kiuwanadmin |
Please make sure you change these passwords as soon as possible, by selecting the option "Account management" from the menu in the upper right corner and selecting "Change Password".
- No labels