| Table of Contents |
|---|
...
New version of CQM
...
(2.0) and Kiuwan Engine
...
| Info |
|---|
Main features of this release are:
|
1. Kiuwan CQM and Engine
A new version of CQM (2.0) has been released. Major changes are:
|
| Info |
|---|
A new version of CQM has been released that incorporate new rules (as detailed below). CQM is the default Model (i.e. a concrete set of active and pre-configured rules):
You can find new rules by comparing this release of CQM against previous version. A detailed description of the behavior of these new rules is available in rule’s description. |
| Info |
|---|
A new version of Kiuwan Engine has been released that incorporates bug fixes, performance and reliability improvements in rules and parsers. Kiuwan Engine is the binary code executed when an analysis is run.
|
Support for cshtml
...
Support for Apache Cordova framework
This new Kiuwan Engine provides support for Apache Cordova framework. Apache Cordova is is a mobile application development framework that enables software programmers to build applications for mobile devices using CSS3, HTML5, and JavaScript, instead of relying on platform-specific APIs like those in Android, iOS, or Windows Phone.
This new Kiuwan Engine provides support for Apache Cordova framework, including new rules that you can find selecting Cordova framework.
Specific rules addressed to Cordova:
- OPT.HTML.CORDOVA.ShouldUseContentSecurityPolicy
- OPT.JAVASCRIPT.CORDOVA.AvoidClickEvent
- OPT.JAVASCRIPT.CORDOVA.AvoidEnabledDebugMode
- OPT.JAVASCRIPT.CORDOVA.InsecureAndroidMinSdkVersion
- OPT.JAVASCRIPT.CORDOVA.TooBroadAccessOrigin
- OPT.JAVASCRIPT.CORDOVA.WhitelistPluginNotInstalled
...
****************************************
Support for ASP.NET Razor C# (cshtml)
Razor is an ASP.NET programming syntax used to create dynamic web pages with the C# or VB.NET programming languages.
...
This new Kiuwan Engine provides provides support for Razor ASP.NET Xamarin platform (Microsoft framework for developing multi-device mobile apps in C# for Android, iOS, MacOS and Windows mobile platforms).
Kiuwan engine is now aware of security-relevant items in Xamarin APIs, providing mappings for input elements in user-defined interfaces (via XAML in Xamarin.Forms) so they are properly considered as user-controlled input.
New Swift security rules
OPT.SWIFT.SECURITY.PasteboardCachingLeak
OPT.SWIFT.SECURITY.PasswordInConfigurationFile
OPT.SWIFT.SECURITY.PotentialInfiniteLoop
OPT.SWIFT.SECURITY.URLSchemeHijacking
OPT.SWIFT.SECURITY.HardcodedUsernamePassword
OPT.SWIFT.SECURITY.PlaintextStorageInACookieRule
OPT.SWIFT.SECURITY.SerializableClassContainingSensitiveData
OPT.SWIFT.SECURITY.ThirdPartyKeyboardAllowed
OPT.SWIFT.SECURITY.UncheckedInputInLoopCondition
OPT.SWIFT.SECURITY.ExecutionAfterRedirect
OPT.SWIFT.SECURITY.SensitiveSQL
OPT.SWIFT.SECURITY.SensitiveNoSQL
OPT.SWIFT.SECURITY.InsecureTemporaryFile
OPT.SWIFT.SECURITY.ConnectionStringParameterPollution
OPT.SWIFT.SECURITY.SensitiveCoreData
OPT.SWIFT.SECURITY.PasswordInCommentRule
OPT.SWIFT.SECURITY.HttpParameterPollutionRule
- OPT.SWIFT.SECURITY.NoSQLInjection
Performance Optimization Guide
If you need to optimize the performance of your local analyses, please read Performance Optimization Guide , a practical how-to guide to optimize the performance and memory consumption of Kiuwan local Analyzer.
2. Insights - Component Dependency Tree
Kiuwan Insights incorporates a new view to better understand the external dependencies of your app.
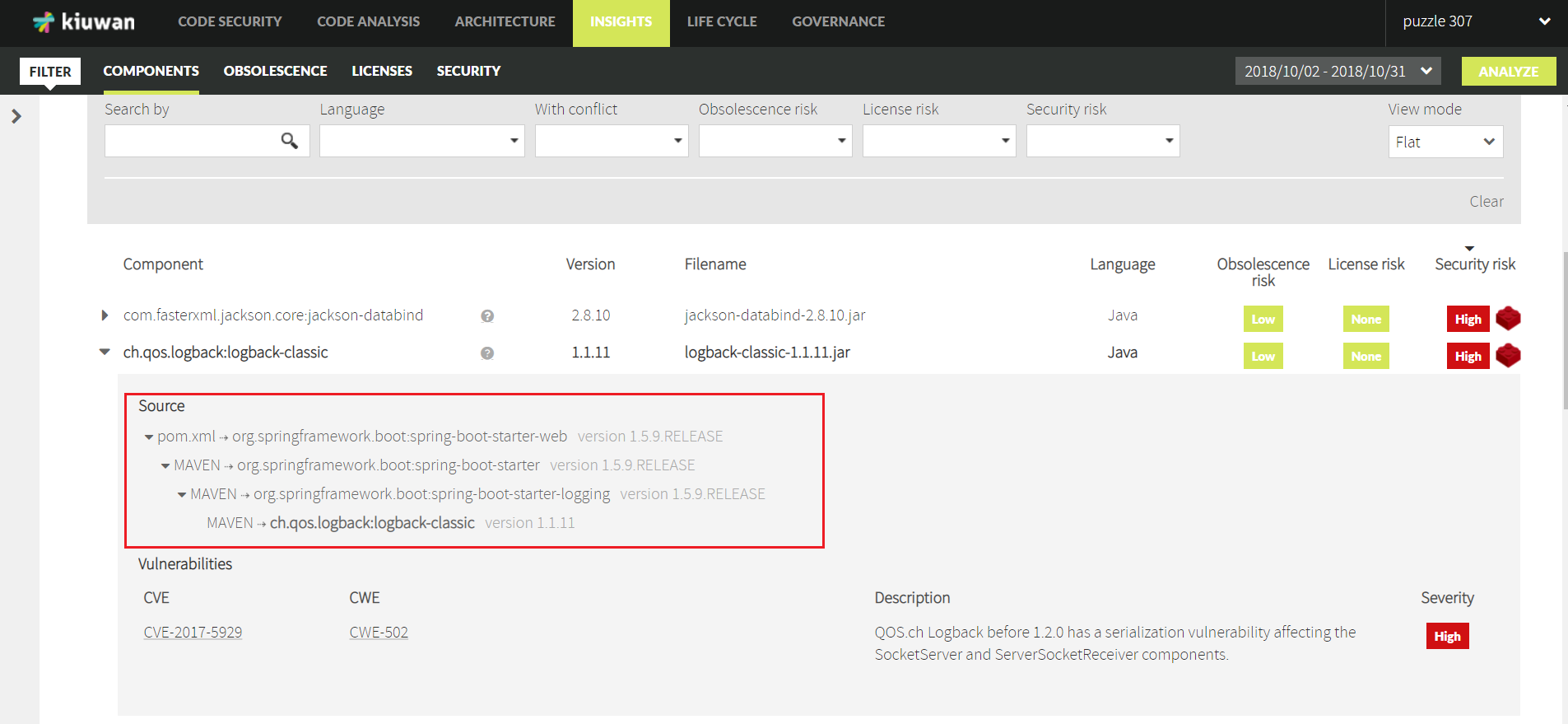
Insights' Component tab let's you now to select a Flat or Tree view of the external components of your application.
By selecting Flat view, you will be able to see the full list of external dependencies (as before), but opening a component you will see the "source" of the dependency, i.e. what's the path that Insights has followed to discover your component.
This Flat view will help you to identify the origin (source) of your dependencies.
For example, in this image you can view that the discovered component (ch.qos.logback:logback-classic) has its origin in a dependency within your pom.xml file which, in turn, contains other transitive dependencies (discovered in Maven repository) until the selected component.
The Flat view, then, displays the whole list of components, directly or indirectly used by your application.
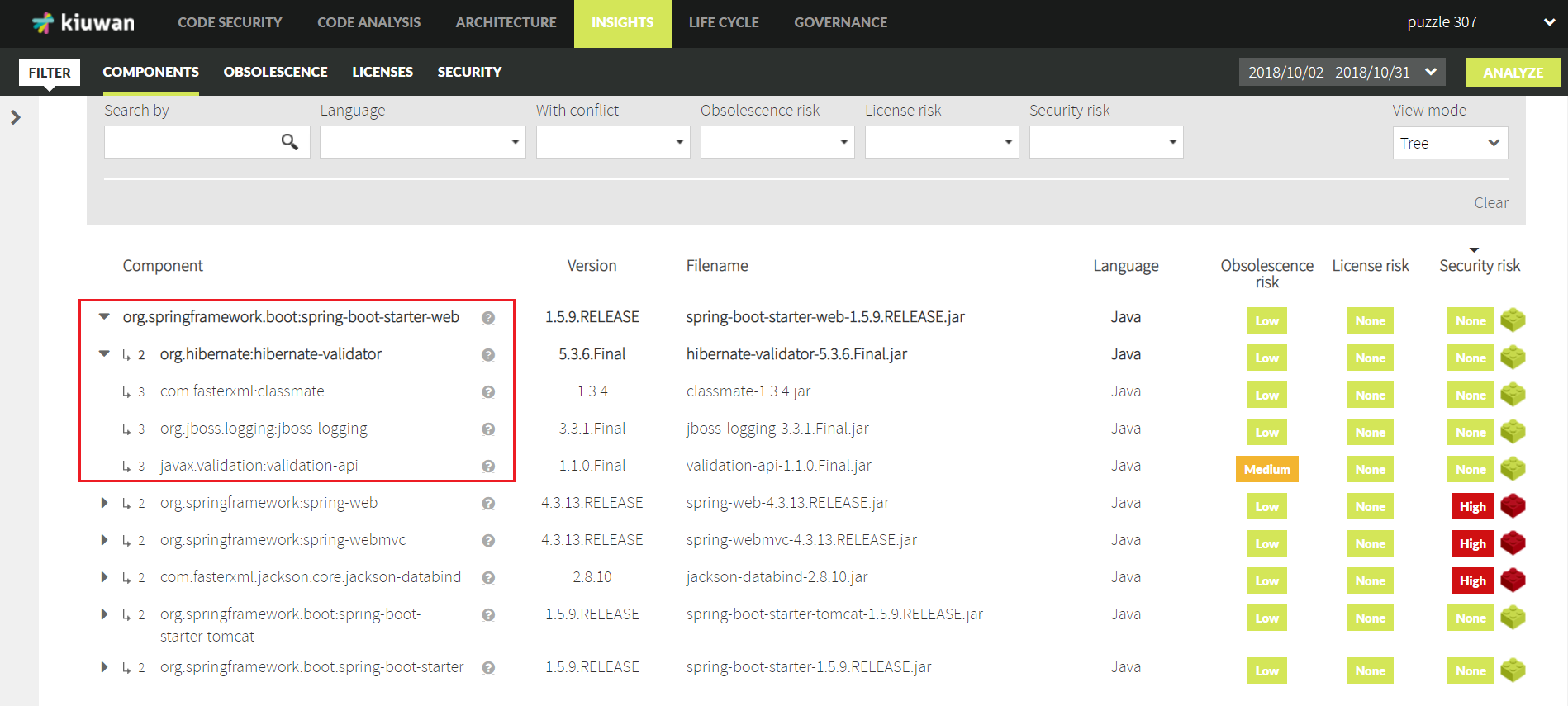
Butm what if you need to know your "direct" dependencies? That is, to know what components are directly used (called) by your application, and be able to drill-down to view the components indirectly used by your application.
The Tree view allows to view your "direct" dependencies as well as the "indirect" dependencies.
The example below shows how the directly-used component "org.springframework.boot:spring-boot-starter-web" (Level 1) uses directly other components (level 2) which, in turn, uses other components (Level 3), and so on.
, providing parsing facilities for .cshtml files.
By being able to process .cshtml files, C# security rules improve its capabilties to detect security vulnerabilties.